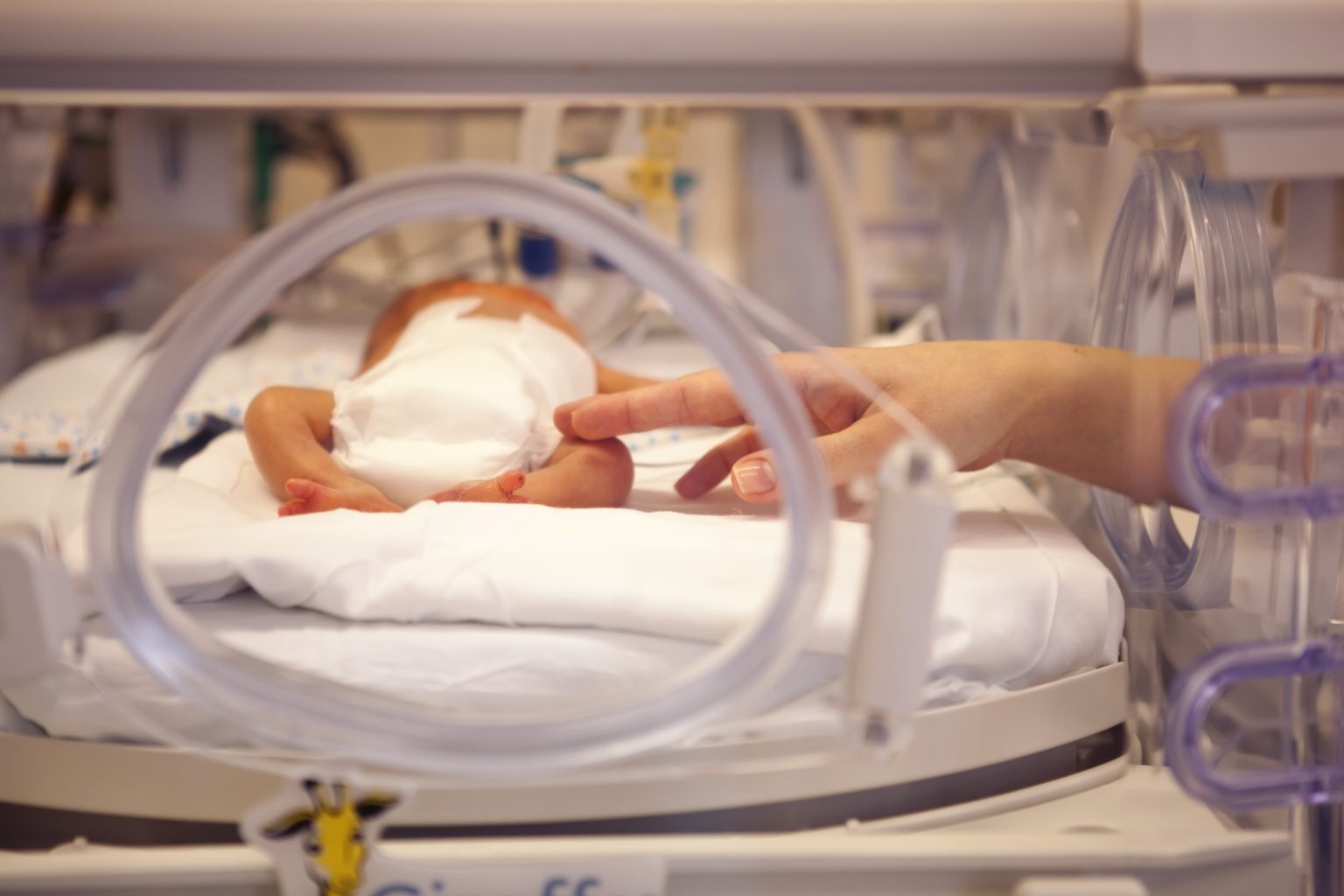
Health can be considered to be a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, without the presence of infirmity or diseases. This often the primary objective of health services, including maternal and child health. The birth weight of a newborn is a good indicator of the status of maternal health. It is also one of the most important factors that determine neonatal mortality and morbidity (newborn death and disease), infant and child morbidity (disease).
Let’s understand what low birth weight means, it’s causes, prevalence, and its diagnosis methods before delivery.
What is low birth weight
It is the term used to describe babies that are born weighing less than 2.5 kilograms. An average newborn baby usually weighs more than 3.5 kg. A low birth weight baby may be healthy at times when the size of the infant is small in general. However, in most of the cases, it can be an indicator of serious health problems.
What causes low birth weight?
It is usually caused by being born too early (prematurely or before 37 weeks of pregnancy). A premature baby has less time to grow and gain weight in the mother’s womb (uterus). Therefore, most of the baby’s weight is gained during the last weeks of pregnancy.
Another cause of low birth weight is IUGR or Intrauterine Growth Restriction. This happens when a baby does not grow well during pregnancy. It may happen due to problems with the placenta, the baby’s health, or the mother’s health. Babies can have IUGR and be premature (characterised by the small size and physical immaturity) and full-term (characterised by a delivery between 37 and 41 weeks of pregnancy with decent physical maturity, yet small in size)
READ: Top 5 Causes of Low Birth Weight in Newborns
Prevalence in India
India has one of the highest proportions of babies born with low birth weight. Estimates suggest that about 7.5 million babies are born underweight in India every year. Many mothers in India from economically weaker backgrounds in suffer from nutritional deficiencies. Some of the ones who are financially equipped to take care of their nutrition, lag due to lack of awareness about including sufficient amounts of calcium and protein in the diet.
Can a doctor diagnose possible low birth weight before delivery
During pregnancy, the size of the baby is estimated in different ways. There are three ways that are usually employed to find out the weight:
-
Monitoring weight gain
This is one way of checking on the baby’s growth.
-
Fundal height
For checking fundal height, the doctor measures from the top of the mother’s pubic bone to the top of the uterus. The fundal height is measured in centimetres and is almost the same as the number of weeks of pregnancy after week 20. For example, at 24 weeks’ gestation, the fundal height should be close to 24 cm. If the fundal height is less than the respective value, it may mean that the baby is not growing well.
-
Fetal ultrasound
It is used to check the baby’s growth and development. Ultrasound uses soundwaves to create a picture of the baby. It is a more accurate way when compared to checking fundal height. Measurements can be taken of the baby’s head, belly (abdomen), and upper leg bone (femur). These measurements are used to estimate the weight of the baby.